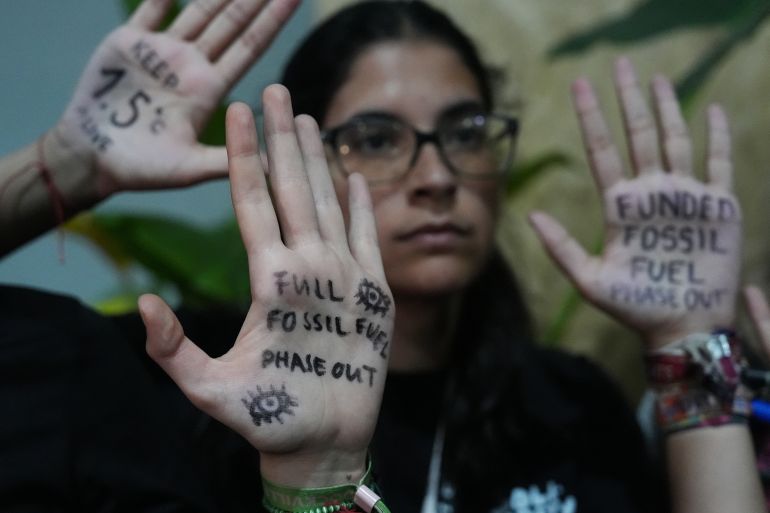UN climate talks go into overtime as divisions over fossil fuels persist
COP30 negotiations drag on in Brazil amid divisions over draft proposal that does not include fossil fuel phase-out.

By Al Jazeera Staff and News Agencies
Published On 21 Nov 202521 Nov 2025
Save
United Nations climate talks in Brazil have gone past their scheduled deadline as countries remain deeply divided over a proposed deal that contains no reference to phasing out fossil fuels.
Negotiators remained in closed-door meetings on Friday evening at the COP30 summit in the Brazilian city of Belem as they sought to bridge differences and deliver an agreement that includes concrete action to stem the climate crisis.
Recommended Stories
list of 3 itemsend of list
A draft proposal made public earlier in the day has drawn concern from climate activists and other experts because it did not contain any mention of fossil fuels – the main driver of climate change.
“This cannot be an agenda that divides us,” COP30 President Andre Correa do Lago told delegates in a public plenary session before releasing them for further negotiations. “We must reach an agreement between us.”
The rift over the future of oil, gas and coal has underscored the difficulties of landing a consensus agreement at the annual UN conference, which serves as a test of global resolve to avert the worst impacts of global warming.
“Many countries, especially oil-producing countries or countries that depend on fossil fuels … have stated that they do not want this mentioned in a final agreement,” Al Jazeera’s Monica Yanakiew reported from Rio de Janeiro on Friday afternoon.
Meanwhile, dozens of other countries have said they would not support any agreement that did not lay out a roadmap to phasing out fossil fuels, Yanakiew noted.
“So this is a big divisive point,” she said, adding that another major issue at the climate conference has been financing the transition away from fossil fuels.
Advertisement
Developing countries – many of which are more susceptible to the effects of climate change, including more extreme weather events – have said they want richer nations to shoulder more of the financial burden of tackling the crisis.
“So there is a lot being discussed … and negotiators say that this might likely continue throughout the weekend,” Yanakiew said.
The deadlock comes as the UN Environment Programme warned ahead of COP30 that the world would “very likely” exceed the 1.5-degree Celsius (2.7-degree Fahrenheit) warming limit – an internationally agreed-upon target set under the Paris Agreement – within the next decade.
Amnesty International also said in a recent report that the expansion of fossil fuel projects threatens at least two billion people – about one-quarter of the world’s population.
In a statement on Friday, Nafkote Dabi, the climate policy lead at Oxfam International, said it was “unacceptable” for any final agreement to exclude a plan to phase out fossil fuels.
“A roadmap is essential, and it must be just, equitable, and backed by real support for the Global South,” Dabi said.
“Developed countries who grew wealthy on their fossil fuel-based economies must phase out first and fastest, while financing low‑carbon pathways for the Global South.”